These references provide a robust framework for understanding the complex dynamics of fund accounting in governmental entities, helping to ensure that financial professionals, policymakers, and academics have access to the most current and comprehensive information. This section explores real-world examples of each type of fund and discusses the decision-making processes involved in determining which fund type to use for specific government operations or projects. These examples illustrate how different funds are utilized in practice and highlight considerations for choosing the appropriate fund type based on the purpose and financial strategy.

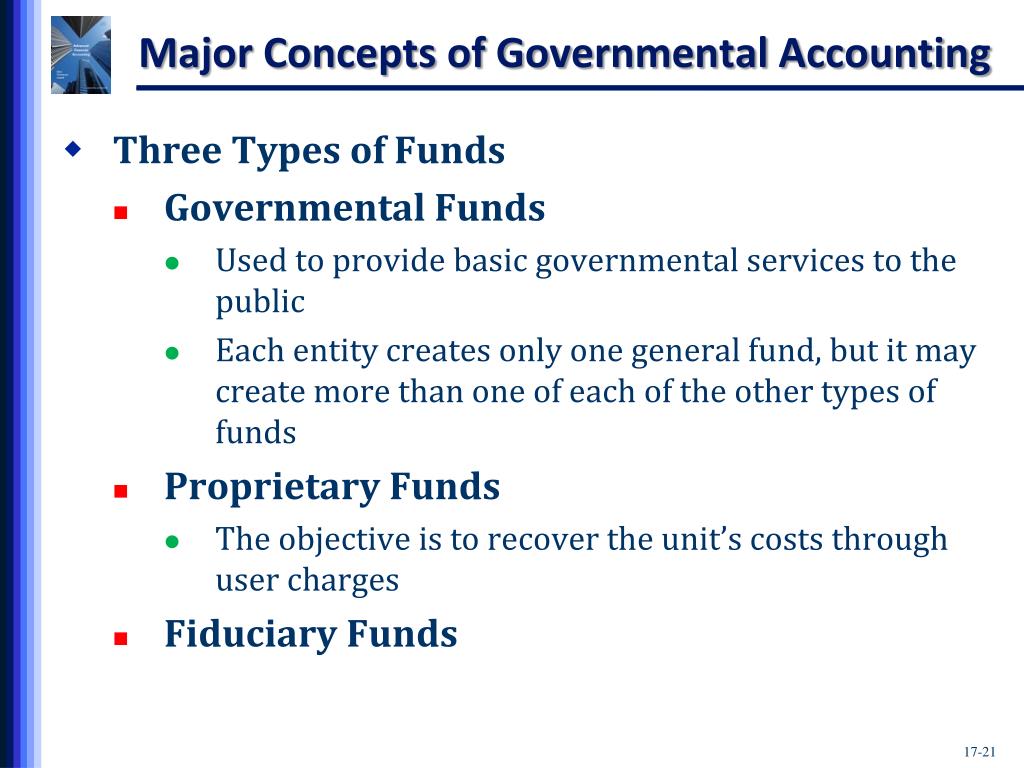
What Are the Different Types of Funds in Government Accounting?
This form of accounting must adhere to strict legal and regulatory standards to ensure that all transactions are lawful and that resources are used appropriately. Code Debt Service Funds – should be used to account for and report financial resources that are restricted, committed, or assigned to expenditure for principal and interest. Financial resources that are being accumulated for principal and interest maturing in future years also should be reported in debt service funds. The debt service transactions for a special assessment for which the government is not obligated in any matter should be reported in a custodial fund. Also, if the government is authorized, or required to establish and maintain a special assessment bond reserve, guaranty, or sinking fund, GASB Statement 6 requires using a debt service fund for this purpose.
Open Capital Assets sub menu
This will likely lead to greater precision in fund tracking and reporting, enabling more dynamic and responsive budgeting processes. Real-world examples and case studies have illustrated how effective fund management supports sustainable financial strategies and public policies, enhancing public services and ensuring fiscal responsibilities are met. Additionally, the role of fund accounting in promoting transparency and building public trust was emphasized, showcasing its importance in public accountability. Proprietary fund statements of net position and revenues, expenses, and changes in fund net position should be presented using the economic resources measurement focus and the accrual basis of accounting. By understanding the nuances and specific requirements of governmental funds, stakeholders can better assess the fiscal health and accountability of governmental entities, ensuring more informed public governance and financial planning.
Appropriation Categories
Authorization acts and appropriation acts provide the legal authority for the government to operate and fund programs or activities. With the use of funds, a governing body is able to establish and monitor how resources are allocated and spent, set and manage spending limits and achieve other fiscal accountability objectives. Similar to any business that operates, governments also establish set accounts in order to achieve certain aims and targets.
REPORT A CONCERN
Fiduciary Funds, on the other hand, manage resources on behalf of others, ensuring ethical stewardship and legal compliance. Each type of fiduciary fund plays a specific role in government financial management, ensuring that resources meant for external beneficiaries are managed with integrity and accountability. By segregating these resources from the government’s own funds, fiduciary funds help maintain trust and meet legal obligations for managing assets on behalf of others. The focus of governmental types of governmental funds funds is on current financial resources, which means assets that can be converted into cash and liabilities that will be paid for with that cash. Stated differently, the balance sheets of governmental funds do not include long-term assets or any assets that will not be converted into cash in order to settle current liabilities. Similarly, these balance sheets will not contain any long-term liabilities, since they do not require the use of current financial resources for their settlement.
- This means that the government records revenue whenever it is available and can be measured.
- The remaining 10 percent of total federal outlays consists of net spending on interest (primarily interest payments on the federal debt).
- Mandatory spending (also called direct spending) consists of outlays for certain federal benefit programs and other payments to individuals, businesses, nonprofit institutions, and state and local governments.
The Debt Service Fund is used to account for and report financial resources that are spent in order to settle different debts. Therefore, this particular type of fund is used in order to account for all debt-related payments and issues within the government. (1) Activities accounted for in governmental funds by function, to coincide with the level of detail required in the governmental fund statement of revenues, expenditures, and changes in fund balances. They may use the calculation below to determine whether an activity would qualify for reporting as a special revenue fund. Debt held by the public is the measure used most often in CBO’s reports on the budget. It is the amount that the government owes to other entities (such as individuals, corporations, state or local governments, the Federal Reserve Banks, and foreign governments).
Kathleen FitzGerald, Ann E. Futrell, Susanne Mehlman, and Emily Stern prepared the report with assistance from Avi Lerner and with guidance from Theresa Gullo, Leo Lex, and Sam Papenfuss. Nathaniel Frentz, Kathleen Gramp, John McClelland, and David Torregrosa of CBO offered comments, as did Kim P. Cawley and Jim Hearn, both formerly of CBO.
The amount by which government outlays exceed revenues in a fiscal year is the deficit. Because the government borrows to finance deficits, a deficit adds to federal debt—the total amount borrowed by the government at a given point in time. Alternatively, a surplus exists when revenues exceed outlays; a surplus reduces federal debt. Budget authority, obligations, and outlays are related terms that describe the funds provided, committed, and used for a program or activity. The purpose of a fund is to set aside a certain amount of money for a specific need. College funds are usually set up by parents to contribute money to a child’s future college education.
The reporting entity is the primary government (including its blended component units) and all discretely presented component units. The government-wide statement of net position and statement of activities should be prepared using the economic resources measurement focus and the accrual basis of accounting. Revenues, expenses, gains, losses, assets, and liabilities resulting from exchange and exchange-like transactions should be recognized when the exchange takes place. Revenues, expenses, assets, and liabilities resulting from nonexchange transactions should be recognized in accordance with the GASB Statements 24 and 33.